
full body kettlebell workout pdf
Kettlebell workouts offer a dynamic, efficient way to engage your entire body, combining strength training and cardiovascular exercise. With a single kettlebell, you can target multiple muscle groups simultaneously, improving coordination, balance, and overall fitness. Their versatility makes them ideal for both beginners and experienced athletes, providing a challenging yet adaptable full-body routine that can be done anywhere, anytime.
What is a Full Body Kettlebell Workout?
A full body kettlebell workout is a comprehensive training method that engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, targeting the entire body in a single session. It combines dynamic movements, strength training, and cardio exercises to improve overall fitness. Unlike traditional weightlifting, kettlebell exercises often involve swinging, pressing, and lifting, which work the arms, legs, core, and back together. This approach enhances coordination, balance, and functional strength while boosting metabolism and burning calories. Full body kettlebell workouts are efficient and versatile, making them ideal for those seeking a time-effective way to build muscle, increase endurance, and improve overall athleticism. They can be adapted to suit various fitness levels, from beginners to advanced trainees.
Benefits of Kettlebell Training for Full Body Development
Kettlebell training offers numerous benefits for full body development, making it a highly effective and efficient workout method. It improves strength, endurance, and flexibility while engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously. The dynamic nature of kettlebell exercises enhances coordination and balance, promoting functional fitness. Additionally, kettlebell workouts are time-efficient, allowing individuals to achieve a comprehensive workout in a shorter duration. They also boost metabolism and burn calories, aiding in weight management. The versatility of kettlebell exercises makes them suitable for all fitness levels, from beginners to advanced athletes. Overall, kettlebell training is a well-rounded approach that enhances overall physical fitness and athletic performance;
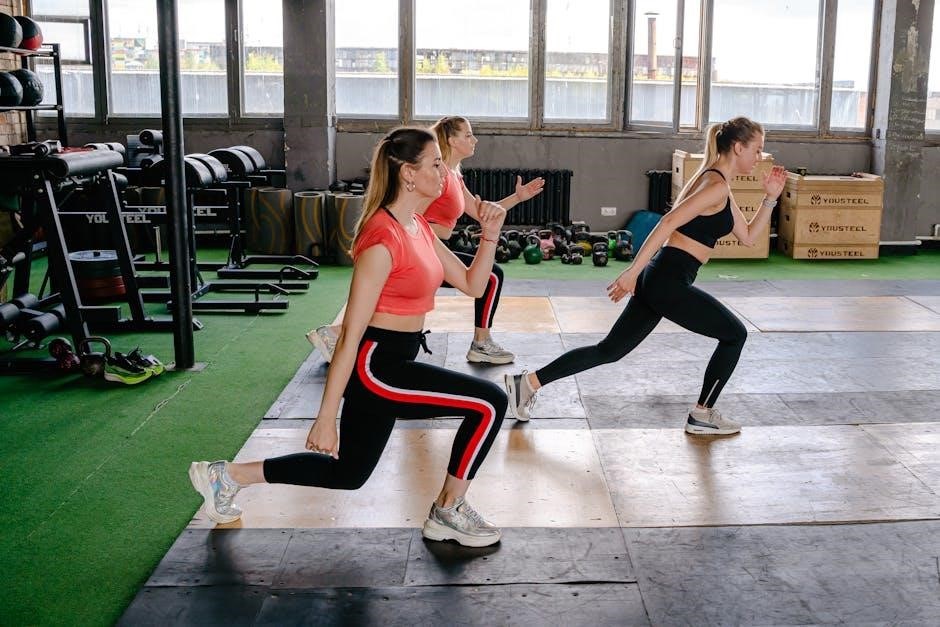
Upper Body Kettlebell Workout
An upper body kettlebell workout targets muscles like shoulders, chest, and back, enhancing strength and endurance. Kettlebell exercises offer versatility and effectiveness for a strong, defined upper physique.
Kettlebell Shoulder Press
The kettlebell shoulder press is an effective exercise for building shoulder strength and overall upper body power. To perform, hold the kettlebell at shoulder height with both hands, elbows bent and close to your body. Press the kettlebell overhead until your arms are fully extended, then lower it back to the starting position. This movement targets the deltoids and triceps, improving overhead strength and stability. Maintain proper form by engaging your core and avoiding arching your back. Start with a moderate weight and gradually increase as you build strength. Incorporate this exercise into your routine for a stronger, more defined upper body.

Kettlebell Side Raise
The kettlebell side raise is a versatile exercise that isolates the lateral deltoids, enhancing shoulder development and stability. Hold the kettlebell with both hands at your sides, palms facing your thighs. Lift the kettlebell to shoulder height, keeping your arms straight and core engaged. Avoid swinging or using momentum, as this can reduce effectiveness and increase injury risk. Focus on controlled movement, squeezing your shoulders at the top. Lower the kettlebell slowly to the starting position and repeat. This exercise improves shoulder balance and aesthetic development. Start with lighter weights to master form before progressing. Incorporate it into your routine for stronger, broader shoulders and enhanced overall upper body symmetry.
Kettlebell Chest Press
The kettlebell chest press is a compound exercise that targets the chest muscles, shoulders, and triceps. Lie on a flat surface, holding the kettlebell with both hands at shoulder height. Press the kettlebell upwards, extending your arms fully while keeping your elbows slightly bent. Lower the kettlebell back to the starting position with controlled movement. This exercise builds chest strength and promotes overall upper body development. Focus on maintaining a neutral spine and engaging your core to prevent arching your back. Incorporate this into your routine for a broader chest and enhanced functional strength. Start with lighter weights to master form before increasing the load for greater intensity.

Kettlebell Bent-Over Row
The kettlebell bent-over row is an effective exercise for targeting the back, shoulders, and biceps. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding the kettlebell with both hands. Bend at the hips and knees, keeping your back straight and core engaged. Let the kettlebell hang straight down, then pull it towards your torso, squeezing your shoulder blades together. Lower the kettlebell back to the starting position with control. This exercise strengthens the latissimus dorsi and improves posture. Focus on maintaining a neutral spine and avoiding rounding of the shoulders. Start with a manageable weight and gradually increase as you build strength and confidence in the movement.
Kettlebell Renegade Row
The kettlebell renegade row is a dynamic exercise that targets the back, shoulders, and core. Start in a plank position with your hands gripping the kettlebell and your feet hip-width apart. Engage your core and maintain a straight line from head to heels. Lift the kettlebell off the ground and row it towards your side, keeping your hips stable. Alternate arms with each rep, ensuring controlled movement throughout. This exercise improves back strength, enhances core stability, and boosts functional fitness; Focus on proper form to avoid straining your lower back. It’s a challenging yet effective movement for building a strong, balanced upper body and improving overall athleticism.

Lower Body Kettlebell Workout
Strengthen your legs, glutes, and core with a lower body kettlebell workout. Improve mobility, power, and overall lower body endurance through dynamic exercises.
Kettlebell Goblet Squat
The kettlebell goblet squat is a foundational exercise for lower body strength. Hold the kettlebell close to your chest with both hands, elbows tucked in. Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly turned out. Lower your body into a squat, keeping your chest upright and knees tracking over your toes. Push through your heels to return to a standing position. This exercise targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes while improving core stability. It’s ideal for building strength and mobility in the lower body. Focus on maintaining proper form to maximize results and prevent injury. The goblet squat is a versatile movement that enhances overall lower body development and coordination.
Kettlebell Swing
The kettlebell swing is a dynamic exercise that targets the posterior chain, including the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back. It involves holding the kettlebell with both hands and swinging it between the legs, then thrusting the hips to propel it forward to shoulder height. This movement improves power, coordination, and cardiovascular fitness. The swing engages multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making it an efficient full-body exercise. Proper form is essential to avoid injury, focusing on a strong hip hinge and maintaining a neutral spine. The kettlebell swing is a cornerstone of kettlebell training, offering both strength and conditioning benefits. It’s a versatile movement for any fitness level.
Kettlebell Clean and Press
The kettlebell clean and press is a powerful exercise that combines strength and coordination, engaging the legs, core, and upper body. Starting with the kettlebell on the ground, it is lifted to the shoulders with a explosive hip drive, mimicking a clean movement; From there, the kettlebell is pressed overhead, extending the arms fully. This exercise improves overall strength, mobility, and coordination. It also enhances power and endurance when performed in higher repetitions. Proper form is critical to avoid injury, focusing on a strong hip hinge during the clean and a stable shoulder position during the press. The kettlebell clean and press is an excellent full-body movement for building functional strength and stamina. It’s versatile, suitable for both beginners and advanced trainees, and can be incorporated into circuits or used as a standalone exercise for targeted development.
Kettlebell Front Squat
The kettlebell front squat is a dynamic exercise that targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core muscles. It involves holding the kettlebell at shoulder height with both hands (often in a rack position) and performing a squat, ensuring proper form by keeping the chest upright and knees tracking over the toes. This exercise improves lower body strength, balance, and mobility. The front load of the kettlebell increases the challenge to the anterior core and promotes better posture. To maximize effectiveness, focus on a full range of motion and controlled movement. The kettlebell front squat is an excellent addition to a full-body workout, offering both strength and functional benefits. It can be performed with one or two kettlebells, depending on the desired intensity.

Full Body Kettlebell Workout
A full-body kettlebell workout combines upper and lower body exercises for total fitness. It enhances strength, endurance, and coordination while burning calories efficiently. Perfect for a balanced routine.

Kettlebell Complexes for Full Body Engagement
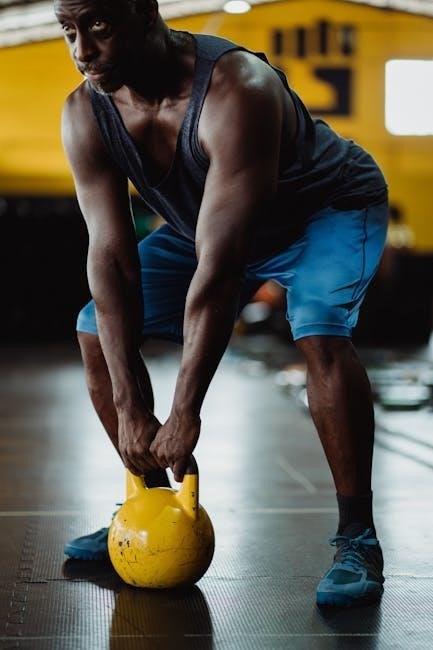

Kettlebell complexes are a series of exercises performed in sequence without rest, targeting multiple muscle groups simultaneously. They are highly efficient and time-saving, engaging the entire body. By combining movements like swings, cleans, presses, and squats in a fluid flow, kettlebell complexes enhance strength, endurance, and coordination. They improve cardiovascular fitness and boost metabolism, making them ideal for full-body conditioning. Complexes can be tailored to different fitness levels by adjusting weight and exercise difficulty. Incorporating them into your routine promotes functional strength and improves overall athleticism. Start with a dynamic warm-up, then focus on maintaining proper form throughout each movement to maximize results and prevent injury.
Kettlebell Circuit Training
Kettlebell circuit training involves performing a sequence of exercises in rapid succession with minimal rest, creating a high-intensity workout. This format is designed to improve cardiovascular fitness, muscular endurance, and metabolic efficiency. By rotating through exercises like kettlebell swings, goblet squats, and presses, you engage multiple muscle groups in a single session. Circuit training is time-efficient and versatile, allowing you to tailor the exercises and intensity to suit your fitness level. It’s an excellent way to burn calories, build strength, and enhance overall physical conditioning. To maximize results, focus on maintaining proper form and gradually increasing the weight or reps as you progress; Circuit training is a dynamic and effective approach to full-body fitness.
Time-Efficient Full Body Kettlebell Routines
Time-efficient full body kettlebell routines focus on maximizing workout productivity by engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously. These routines often incorporate compound exercises like kettlebell swings, goblet squats, and shoulder presses, which target the legs, core, and upper body effectively. A typical routine might involve a circuit of 4-5 exercises, each performed for 5-7 minutes, allowing for minimal rest between sets. This structure not only saves time but also enhances cardiovascular fitness and muscular endurance. To ensure progression, increase the weight or reps as you build strength. Always include a brief warm-up and cool down to prepare and recover. These routines are ideal for those seeking a comprehensive yet concise workout.
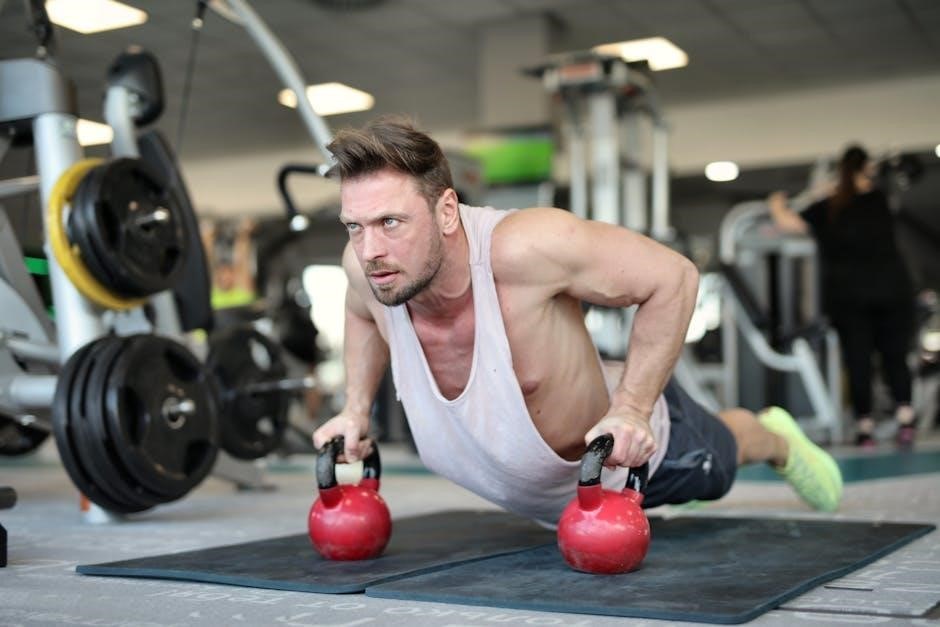

Creating a Kettlebell Workout Plan
A well-structured kettlebell workout plan involves defining fitness goals and selecting exercises that target all muscle groups. Balance upper and lower body workouts with core exercises. Start with basic movements, gradually increasing intensity and complexity. Tailor routines to suit individual fitness levels and objectives. Plan for consistency, ensuring adequate recovery time between sessions. Regularly assess progress and adjust the plan to avoid plateaus and maintain motivation. A thoughtfully designed plan ensures efficient and sustainable fitness improvements over time;
Determining Sets and Reps for Maximum Efficiency
For a full-body kettlebell workout, sets and reps should align with your fitness goals. Endurance training typically involves 12-15 reps per set, while strength-focused workouts use 3-6 reps. Hypertrophy goals often fall between 8-10 reps. Start with 3-4 sets per exercise, adjusting based on fitness level. Increase reps or sets as strength improves. Rest periods should be minimized for efficiency, ideally 30-60 seconds between sets. Consistency is key to achieving desired results. Tailor your approach to ensure progressive overload, gradually increasing intensity over time. This structured method ensures your kettlebell workout remains effective and challenging, promoting continuous improvement. Adjustments should be made based on individual progress and goals.
Progression and Scaling Your Kettlebell Workout
Progression and scaling are essential for continuous improvement in kettlebell training. Start with lighter weights and focus on mastering form before increasing load. Gradually add weight or reps as strength and endurance improve. For scaling, modify exercises to suit fitness levels, such as switching from a kettlebell swing to a deadlift or adjusting range of motion. Incorporate variations like single-arm or alternating movements to challenge different muscle groups. Periodically test maximum reps or weight to track progress. Adjust rest periods or intensity to keep workouts challenging. Consistent progression ensures long-term success and prevents plateaus, helping you achieve a well-rounded full-body fitness regimen effectively.
Warm-Up and Cool Down Techniques
A proper warm-up and cool-down are crucial for optimizing kettlebell workouts and preventing injury. Begin with dynamic stretching, such as arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, to activate major muscle groups. Add light cardio like jumping jacks or kettlebell swings at a low intensity to elevate heart rate and prepare the body for exertion. After training, cool down with static stretches targeting the shoulders, hamstrings, and quadriceps to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension. Incorporate deep breathing exercises to promote relaxation and aid recovery. Foam rolling can also be used to release muscle tightness. A well-structured warm-up and cool-down routine enhances performance and supports overall recovery, ensuring a safe and effective full-body kettlebell workout experience. Always prioritize these steps to maintain consistency and progress in your fitness journey.
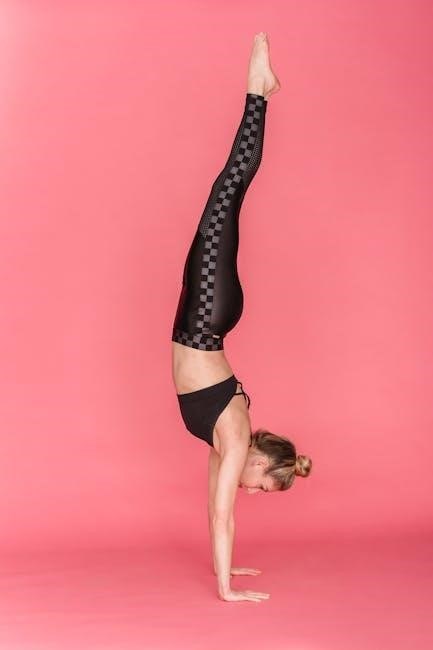

Kettlebell Workout Tips for Beginners
Start with lighter weights to master form, focus on compound movements, and pace yourself to avoid fatigue. Stay consistent, track progress, and remain patient for best results.
Choosing the Right Kettlebell Weight
When selecting a kettlebell weight, start light to focus on proper form and technique. Beginners should opt for 8-12 kg for women and 12-16 kg for men. Consider your fitness level, strength, and the exercises you’ll perform. Lighter weights are ideal for dynamic movements like swings, while slightly heavier bells may be used for presses or squats. Avoid overly heavy weights that compromise form, as this increases injury risk. Gradually increase the weight as your strength and confidence grow. The right weight allows you to maintain control throughout the exercise, ensuring safety and effectiveness. Prioritize technique over load initially for optimal results.
Mastering Proper Form and Safety
Proper form is essential for maximizing results and preventing injuries in kettlebell workouts. Always engage your core and maintain a neutral spine to protect your back. Keep the kettlebell close to your body during lifts to reduce strain. Avoid rounding your shoulders or using excessive momentum, as this can lead to poor form and potential harm. Start with slower, controlled movements to build muscle memory and coordination. Warm up thoroughly before each session and cool down afterward to prevent muscle tightness. Ensure you have enough space to perform swings and other dynamic movements safely. Focus on smooth transitions between exercises to maintain balance and stability; Prioritizing form ensures a safe and effective workout experience.
Nutrition and Recovery for Optimal Results
Nutrition and recovery are critical for achieving the best results from your full-body kettlebell workout. Ensure a balanced diet rich in protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel your sessions and support muscle repair. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water before, during, and after workouts. Post-workout, consume a meal or shake with protein and carbs within an hour to aid recovery. Prioritize sleep, aiming for 7-9 hours nightly, as it is vital for muscle regeneration and overall performance. Incorporate active recovery techniques, such as stretching or yoga, to reduce muscle soreness. Allow at least 48 hours of rest between intense workouts targeting the same muscle groups. Supplements, like whey protein or BCAAs, can also support recovery, though they should complement, not replace, a healthy diet.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.